Table of Contents
Aim:
To perform the limit test for heavy metals for the given sample.
Requirements:
Nessler cylinders, 1ml bulb pipette, dilute acetic acid, dilute ammonia solution, hydrogen sulphide solution, pH paper: 3-4 range, lead standard solution (20 ppm Pb), glass rods.
Principle:
In this experiment, the test color obtained by the reaction of heavy metal impurities with a saturated solution of hydrogen sulphide is compared with the standard color obtained by the reaction of a known quantity of lead with a saturated solution of hydrogen sulphide.
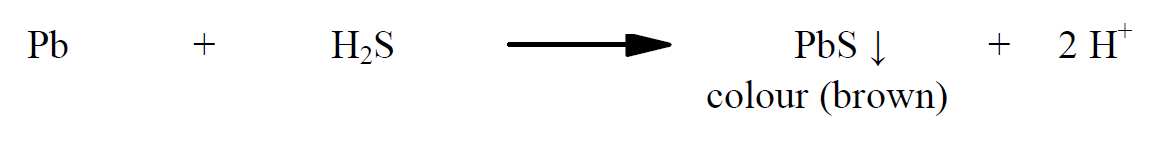 The precipitate of heavy metal sulphide formed gives colour. Dilute acetic acid and ammonia are used to maintain pH between 3.0 and 4.0 so that the precipitate formed is colloidal and uniform. The saturated solution of hydrogen sulphide has to be prepared freshly for the experiment. Here hydrogen sulphide gas is generated using a specially devised apparatus called as Kipp’s apparatus in which ferrous sulphide sticks are made to react with equal volumes of concentrated hydrochloric acid and water. Indian pharmacopeia 1996, provides four methods depending on the resulting solution of substance (i.e., based on solubility, colour etc). Method A uses hydrogen sulphide solution, method B uses hydrogen sulphide solution after igniting the substance, method C uses sodium sulphide solution after treating the substance with sodium hydroxide solution, and in method D thioacetamide solution is used. In a concise way, the methods can be categorized as follows:
The precipitate of heavy metal sulphide formed gives colour. Dilute acetic acid and ammonia are used to maintain pH between 3.0 and 4.0 so that the precipitate formed is colloidal and uniform. The saturated solution of hydrogen sulphide has to be prepared freshly for the experiment. Here hydrogen sulphide gas is generated using a specially devised apparatus called as Kipp’s apparatus in which ferrous sulphide sticks are made to react with equal volumes of concentrated hydrochloric acid and water. Indian pharmacopeia 1996, provides four methods depending on the resulting solution of substance (i.e., based on solubility, colour etc). Method A uses hydrogen sulphide solution, method B uses hydrogen sulphide solution after igniting the substance, method C uses sodium sulphide solution after treating the substance with sodium hydroxide solution, and in method D thioacetamide solution is used. In a concise way, the methods can be categorized as follows:
Method I: It is used for the substance which gives a clear, colorless solution under specified conditions.
Method II: It is used for the substance which does not give a clear, colorless solution.
Method III: It is used for the substance which gives a clear, colorless solution in sodium hydroxide medium
Procedure:
Test color:
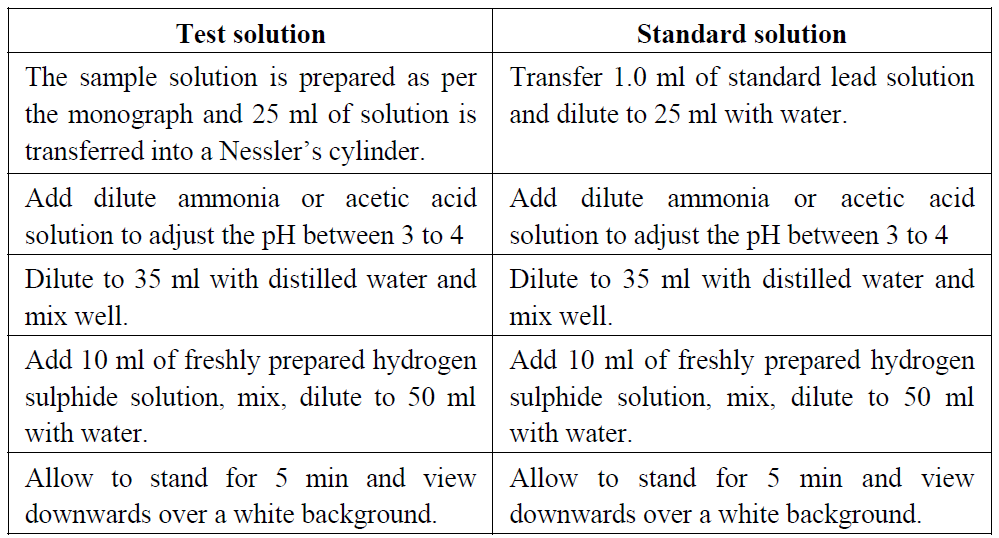
Dissolve the given sample in 25 ml of water and transfer into a Nessler cylinder. Adjust with dilute acetic acid or dilute ammonia solution to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to about 35 ml and mix. Add 10 ml of freshly prepared hydrogen sulphide solution, mix, dilute to 50 ml with water, allow to stand for 5 minutes, and view downwards over a white surface. Standard colour: Pipette 1.0 ml of lead standard solution (20 ppm Pb) into a Nessler cylinder and dilute with water to 25 ml. Adjust with dilute acetic acid or dilute ammonia solution to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to about 35 ml and mix. Add 10 ml of freshly prepared hydrogen sulphide solution, mix, dilute to 50 ml with water, allow to stand for 5 minutes, and view downwards over a white surface.
Method I: It is used for the substance which gives a clear, colorless solution under specified conditions.
Method II: It is used for the substance which does not give a clear, colorless solution.
Method III: It is used for the substance which gives a clear, colorless solution in sodium hydroxide medium.
Observation:
If the color produced in the test solution is not more intense than that of standard solution, the sample complies with the standards of I.P or vice versa.
Test colour is not more intense than standard colour.
or
Test colour is more intense than standard colour.
Report/Result:
The given sample passes limit test for heavy metals.
or
The given sample fails limit test for heavy metals.
Preparation of Reagents:
1. Dilute acetic acid: Contains approximately 6% w/w of CH3COOH. Dilute 57 ml of glacial acetic acid to 1000 ml with water.
2. Dilute ammonia solution: Contains approximately 10% w/w of NH3. Dilute 425 ml of strong ammonia solution to 1000 ml. Store in well-closed containers in a cool place.
3. Lead Standard solution (0.1% Pb): Dissolve 0.400 g of lead nitrate in water containing 2 ml of nitric acid and add sufficient water to produce 250.0 ml.
4. Lead Standard solution (100 ppm Pb): Dilute 1 volume of lead standard solution (0.1% Pb) to 10 volumes with water.
5. Lead Standard solution (20 ppm Pb): Dilute 1 volume of lead standard solution (100 ppm Pb) to 5 volumes with water.
References
https://www.bspublications.net/downloads
/059cc8f84560f2_Ch 1_Subba%20Rao_Practical%20
Pharmaceutical%20In-organic%20Chemistry.pdf
https://lms.jspmjscopr.edu.in/mod/resource/view.php?id=2792
https://www.pharmaguideline.com/2008/06/method-of-analysis-
for-calcium-carbonate.html
https://www.coursehero.com/file/p5ipvs6k/3–Dithizone
-extraction-solution-Dissolve-30-mg-of-dithizone-in-1000-ml-of/
Also Read :










[…] Limit Test for Heavy Metals […]
[…] Limit Test for Heavy Metals […]