Table of Contents
Introduction
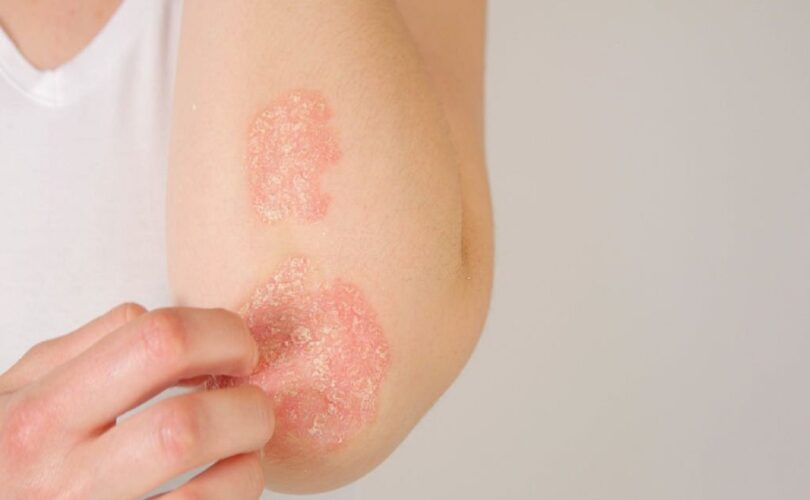
Ah, eczema. The gift that keeps on giving. It’s a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide and is responsible for countless hours of itching, scratching, and general discomfort. For those of you lucky enough not to know, eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes red, itchy, and scaly patches to develop on various parts of the body. Lucky us! The prevalence of eczema is increasing, with up to 1 in 5 children and 1 in 12 adults affected. If that doesn’t make you scratch your head, then the impact on physical and mental health will! Stay tuned for more fun facts..
Symptoms of Eczema
So, you’re feeling itchy and you’ve got red patches on your skin. Could it be eczema? Well, it’s definitely a possibility. Eczema is a common skin condition and there are a few types you should know about. Atopic dermatitis is the most common form and usually appears in childhood. It’s often associated with allergies and asthma. Contact dermatitis is caused by an allergen or irritant coming into contact with the skin. Nummular eczema appears as round plaques and can be quite itchy. Dyshidrotic eczema affects the hands and feet and is particularly annoying because the tiny blisters it causes can be itchy and painful. Now, let’s move on to the symptoms of eczema. Common symptoms include dry, itchy skin that may be accompanied by redness and small bumps. When the skin is scratched, it can become leathery and thick. Severe eczema can cause a lot of discomfort for sufferers, with symptoms such as extensive dryness, blistering, and even bleeding. To manage eczema, it’s important to identify the triggers and avoid them. Moisturizing regularly, avoiding irritants and allergens, and treating infections promptly are key steps to avoiding severe symptoms. Topical corticosteroids can be applied to the affected area to reduce inflammation, while phototherapy and systemic medication can be used in more severe cases. Overall, eczema can be managed effectively with proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention techniques. It’s important to identify any triggers and adjust your lifestyle accordingly to manage symptoms.
Pathophysiology of Eczema
So, eczema, huh? The pathophysiology of this condition is quite interesting. It is characterized by the breakdown of the skin barrier, making it more susceptible to irritants and allergens. But what causes this breakdown, you may ask? Well, it’s a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Let’s start with genetics. Turns out, certain genes make you more prone to eczema, and it tends to run in families. So, thanks, Mom and Dad, for the eczema gene pool! But it’s not just about the genes, as environmental factors play a role too. The immune system, in particular, plays a key role in eczema pathophysiology. The immune system of individuals with eczema tends to overreact to certain triggers, causing inflammation and itchiness. This can make the skin more vulnerable to infections and further exacerbate the condition. Talk about a vicious cycle. So, to summarize, eczema is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, with the immune system playing a key role in its pathophysiology. But don’t worry, we’ll cover how to prevent and manage this pesky condition in the following sections.
Diagnosis of Eczema
Diagnosing eczema can be a bit tricky as the symptoms can be similar to other skin conditions. However, doctors usually perform a physical examination to determine eczema. During the examination, they check the symptoms and ask about the patient’s medical history. Skin patch tests and blood tests are also used to diagnose eczema. Skin patch tests involve placing a patch on the skin with suspected allergens for two days to determine if there is a reaction. Meanwhile, blood tests look for antibodies in the blood that indicate an allergic reaction. It’s important to get an accurate diagnosis to help treat eczema effectively.
Treatment of Eczema
So, let’s talk about the treatment of eczema. While there is no cure for eczema, there are several ways to manage the symptoms and prevent flare-ups. First things first, let’s focus on moisturizers and skin care. Keeping your skin moisturized is essential in managing eczema. Use a fragrance-free, non-greasy moisturizer regularly to keep your skin hydrated. And make sure to apply it right after a bath or shower, when your skin is still damp, to help lock in moisture. Simple, but effective! If your eczema is more severe, your doctor may prescribe topical corticosteroids. This medication can help reduce inflammation and itching in affected areas. It’s important to use only as directed and not apply to the face or groin area unless specifically instructed to by your doctor. Another option for more severe cases is phototherapy or systemic medication. Phototherapy involves exposing the affected area to controlled amounts of UVB light, which can improve symptoms. Systemic medication, like immunosuppressants or biologics, work to suppress the immune system’s response, which can lessen inflammation and irritation. However, these medications tend to have more side effects and are typically reserved for severe cases. Lastly, wet wrap therapy is an option for those who experience significant itching at night. It involves applying a moisturizer to the affected area and then wrapping it in wet gauze or clothing. This can help hydrate and soothe the skin while preventing scratching and further damage. Overall, the treatment of eczema depends on the severity of the symptoms, so be sure to discuss options with your doctor to find what works best for you. Remember, consistent skin care and moisturizing are key in preventing flare-ups and managing eczema.
Prevention of Eczema
So, you have eczema and you’re wondering what you can do to prevent it from flaring up? Well, you’re in luck because we’ve got some tips for you. First off, it’s important to identify the triggers that cause your eczema to flare up. Is it stress? Certain foods? Allergens? Knowing your triggers can help you avoid them, or at least be better prepared when exposed to them. Next, you’ll want to keep your skin moisturized. This means using gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers regularly, especially after showering or washing your hands. Dry skin can worsen eczema symptoms, so it’s important to stay moisturized. Avoiding irritants and allergens is also crucial in preventing eczema flare-ups. This may mean switching to gentler skincare products or avoiding certain fabrics or materials that cause skin irritation. Be sure to also keep an eye out for any signs of infection and treat them promptly to prevent eczema from getting worse. Remember, prevention and management of eczema involves making lifestyle changes that work for you. Unfortunately, there is no cure for eczema, so it’s important to take the necessary steps to prevent flare-ups.
Conclusion
So, to summarize, eczema is a skin condition that impacts physical and mental health. It’s important to identify triggers, keep the skin moisturized, avoid irritants/allergens, and treat infections promptly. Treatment options include moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, systemic medication, and wet wrap therapy. Early treatment and prevention are vital. Don’t wait until it’s too late to take care of your skin, folks. Stay moisturized, stay healthy!